Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Calculation of revenues¶
We use an estimated model to calculate revenues.
Michel Bierlaire, EPFL Sat Jun 28 2025, 18:57:49
import sys
import numpy as np
from biogeme.biogeme import BIOGEME
from biogeme.models import nested
from biogeme.results_processing import EstimationResults
try:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
can_plot = True
except ModuleNotFoundError:
can_plot = False
from biogeme.data.optima import read_data, normalized_weight
from scenarios import scenario
Read the estimation results from the file.
try:
results = EstimationResults.from_yaml_file(
filename='saved_results/b02estimation.yaml'
)
except FileNotFoundError:
sys.exit(
'Run first the script b02simulation.py '
'in order to generate the '
'file b02estimation.yaml.'
)
Read the data
database = read_data()
Function calculating the revenues
def revenues(factor: float) -> tuple[float, float, float]:
"""Calculate the total revenues generated by public transportation,
when the price is multiplied by a factor.
:param factor: factor that multiplies the current cost of public
transportation
:return: total revenues, followed by the lower and upper bound of
the confidence interval.
"""
filename = f'revenue_{factor:.2f}.txt'
SEPARATOR = '%'
try:
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
line = f.read()
revenue, left, right = line.split(SEPARATOR)
return float(revenue), float(left), float(right)
except FileNotFoundError:
...
# Obtain the specification for the default scenario
utilities, nests, _, marginal_cost_scenario = scenario(factor=factor)
# Obtain the expression for the choice probability of each alternative
prob_pt = nested(utilities, None, nests, 0)
# We now simulate the choice probabilities,the weight and the
# price variable
simulate = {
'weight': normalized_weight,
'Revenue public transportation': prob_pt * marginal_cost_scenario,
}
the_biogeme = BIOGEME(database, simulate)
simulated_values = the_biogeme.simulate(results.get_beta_values())
# We also calculate confidence intervals for the calculated quantities
beta_bootstrap = results.get_betas_for_sensitivity_analysis()
left, right = the_biogeme.confidence_intervals(beta_bootstrap, 0.9)
revenues_pt = (
simulated_values['Revenue public transportation'] * simulated_values['weight']
).sum()
revenues_pt_left = (left['Revenue public transportation'] * left['weight']).sum()
revenues_pt_right = (right['Revenue public transportation'] * right['weight']).sum()
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
print(
f'{revenues_pt} {SEPARATOR} {revenues_pt_left} {SEPARATOR} {revenues_pt_right}',
file=f,
)
return revenues_pt, revenues_pt_left, revenues_pt_right
Current revenues for public transportation
r, r_left, r_right = revenues(factor=1.0)
print(
f'Total revenues for public transportation (for the sample): {r:.1f} CHF '
f'[{r_left:.1f} CHF, '
f'{r_right:.1f} CHF]'
)
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.38it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.25it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.22it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.21it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.22it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.22it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.22it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.22it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.24it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.24it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.21it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.22it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.19it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.21it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.19it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.19it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.20it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.20it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.19it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.19it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.20it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.20it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.20it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.20it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.19it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.20it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.21it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.23it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.20it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.21it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.22it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.23it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:27, 2.41it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:23, 2.76it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:20, 3.08it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.35it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.56it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.74it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.88it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 3.98it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.06it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.11it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.15it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.18it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.20it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.22it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.22it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.22it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.22it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.22it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.19it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.15it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:11, 3.93it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:11, 3.89it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:11, 3.88it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 3.96it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.02it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.02it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.01it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.01it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.07it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.11it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.10it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.08it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.08it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.08it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.08it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:13, 2.28it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:11, 2.62it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:09, 2.92it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.22it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:07, 3.43it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.61it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.72it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.85it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 3.92it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.98it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.04it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.03it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.05it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.04it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.05it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.06it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.08it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.07it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.08it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.08it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.12it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.15it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.12it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.11it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.13it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.15it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.13it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.13it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.09it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.11it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.07it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.10it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.94it/s]
Total revenues for public transportation (for the sample): 3043.3 CHF [2423.5 CHF, 3643.7 CHF]
We now investigate how the revenues vary with the multiplicative factor
factors = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.1)
plot_revenues = [revenues(s) for s in factors]
zipped = zip(*plot_revenues)
rev = next(zipped)
lower = next(zipped)
upper = next(zipped)
largest_revenue = max(rev)
max_index = rev.index(largest_revenue)
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.35it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<01:03, 1.53it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:45, 2.15it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:36, 2.64it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:31, 3.03it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:28, 3.34it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:25, 3.58it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:25, 3.60it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.69it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.78it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.88it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.97it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.08it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.10it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.16it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.20it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.20it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.23it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.22it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.02it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 3.98it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.01it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.06it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.10it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.16it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.12it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.15it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.18it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.16it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.20it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.23it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.18it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.22it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.25it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:27, 2.32it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:23, 2.70it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:20, 3.03it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:20, 3.06it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:18, 3.33it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:17, 3.48it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.61it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.56it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.70it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.77it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.79it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.76it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.79it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.90it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.99it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.07it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.07it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.08it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.06it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.06it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.09it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.16it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.20it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.26it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.32it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.35it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.36it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.33it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.33it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.32it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.33it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.34it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.32it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.35it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.23it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:12, 2.33it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:10, 2.70it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.03it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.30it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.58it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.67it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.76it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.85it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.98it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.08it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.13it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.19it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.24it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.23it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.22it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.24it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.22it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.19it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.14it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.07it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.03it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.07it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.10it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.09it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.15it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.17it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.22it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.22it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.19it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.21it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.19it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.83it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.90it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<01:05, 1.49it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:46, 2.11it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:37, 2.59it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:31, 2.98it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:28, 3.28it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:26, 3.52it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.70it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.80it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.88it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.96it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.99it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.99it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.02it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.03it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.06it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.08it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:20, 4.07it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.05it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.06it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.06it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.89it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.88it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.55it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.62it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.69it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.77it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.83it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.87it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.90it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.92it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.91it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.95it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.93it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.98it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:29, 2.16it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:25, 2.49it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:22, 2.80it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:19, 3.07it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:18, 3.29it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.48it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:16, 3.62it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.70it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.79it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.85it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.88it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.89it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.89it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.94it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.97it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:12, 4.00it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.05it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.08it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:11, 4.05it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:11, 4.09it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.09it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.79it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.44it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.57it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.65it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.72it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.77it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.86it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.90it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.90it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.92it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.90it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.89it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:15, 2.06it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:12, 2.39it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:10, 2.70it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:09, 2.99it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.21it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:07, 3.40it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:07, 3.53it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.67it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.71it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.75it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.84it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.83it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.79it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.79it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.80it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.79it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.80it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.78it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.80it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.88it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.91it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.95it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.99it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.05it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.07it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:26<00:01, 4.05it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 4.05it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.07it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.10it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.07it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.08it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.00it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.62it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:01<01:44, 1.05s/it]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<00:57, 1.72it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:42, 2.31it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:34, 2.75it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:30, 3.12it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:27, 3.39it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:25, 3.60it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.75it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.87it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.97it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:22, 4.03it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.06it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.00it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.98it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.02it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.05it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:20, 4.00it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.96it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.92it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.90it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.97it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.02it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.98it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.96it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.95it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.86it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.90it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.93it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.93it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.78it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.70it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.73it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.75it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:10<00:33, 1.97it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:27, 2.32it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:24, 2.62it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:11<00:21, 2.89it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:19, 3.14it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:18, 3.38it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:17, 3.49it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:12<00:16, 3.58it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.71it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.75it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.74it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.76it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.73it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.75it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.75it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:14<00:13, 3.76it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:13, 3.73it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.77it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.76it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.78it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.81it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.88it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.95it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.96it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.95it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.87it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.92it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.95it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.98it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.00it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.00it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.03it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.93it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:15, 2.07it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:13, 2.43it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:11, 2.77it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:20<00:09, 3.05it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.28it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.49it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.64it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.77it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.87it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.93it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.89it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.87it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.85it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.90it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.89it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.88it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.90it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.95it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.96it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.97it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.98it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.99it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.99it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.92it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.90it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.89it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.88it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.84it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.52it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.61it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.72it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.84it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.91it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.95it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.58it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:01<01:40, 1.02s/it]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<00:55, 1.78it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:40, 2.41it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:33, 2.87it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:29, 3.22it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:27, 3.48it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:25, 3.68it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.82it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.88it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.92it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.93it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.00it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.03it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.06it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.09it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.07it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.08it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:20, 4.08it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.06it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.07it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.07it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.08it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.08it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.07it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.05it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.01it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.04it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.98it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.01it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.03it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.04it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.07it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.07it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.10it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:30, 2.11it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:27, 2.36it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:25, 2.50it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:22, 2.79it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:19, 3.08it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:18, 3.33it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.54it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.69it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.79it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.89it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.97it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.99it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 4.03it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.06it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.09it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.11it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.12it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.13it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.13it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.12it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.12it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.12it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.13it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.14it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.14it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.14it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.10it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.12it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.12it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.14it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.13it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.13it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.13it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:14, 2.14it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:11, 2.51it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:10, 2.85it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.14it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.39it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.58it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.73it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.83it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.91it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.99it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.04it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.06it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.07it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.10it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.11it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.10it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.10it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.13it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.12it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.10it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.10it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.08it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.10it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.13it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.12it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.14it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.10it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.11it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.12it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.16it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.15it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.18it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.73it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.23it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<01:08, 1.43it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:47, 2.04it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:37, 2.56it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:32, 2.96it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:28, 3.29it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:26, 3.51it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.72it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.85it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.92it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.97it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.02it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.05it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.09it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.11it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.11it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.08it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.10it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.11it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.11it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.12it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.09it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.09it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.07it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.06it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.06it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.10it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.11it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.12it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.12it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.14it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.16it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.15it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.15it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.15it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:30, 2.10it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:25, 2.47it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:22, 2.81it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:19, 3.11it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:17, 3.37it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.56it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.70it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.81it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.92it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.99it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.03it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.07it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.86it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.83it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.92it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.97it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.00it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.04it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.06it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.05it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.06it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.08it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.08it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.07it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.09it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.07it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.08it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.05it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.07it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.07it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.07it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.08it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.11it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.13it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:14, 2.07it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:11, 2.43it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:10, 2.76it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.06it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.31it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.53it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.68it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.60it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.73it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.85it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.92it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.96it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.00it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.04it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.06it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.08it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.09it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.09it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.10it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.11it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.11it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.13it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.13it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.08it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.09it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.07it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.06it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.06it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.07it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.09it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.09it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.73it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.10it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.09it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<01:04, 1.51it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:47, 2.01it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:38, 2.45it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:33, 2.83it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:29, 3.15it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:29, 3.12it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:26, 3.38it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:25, 3.57it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.72it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.84it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:22, 3.94it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.01it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.04it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.05it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:20, 4.08it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.10it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.10it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.08it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.08it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.10it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.09it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.06it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.07it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.06it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.07it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.09it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.06it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.05it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.05it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.04it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.06it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.06it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.99it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.99it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.01it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:31, 1.97it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:26, 2.33it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:22, 2.67it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:19, 2.97it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:17, 3.23it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:16, 3.43it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.60it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.74it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.84it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.90it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.93it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.99it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:12, 4.02it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:12, 4.02it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.04it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.02it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:11, 4.04it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.98it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.99it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.01it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.99it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.98it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.94it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.97it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.98it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.01it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.02it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.01it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.00it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.02it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.03it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.03it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.01it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.03it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.04it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:13, 1.99it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:11, 2.35it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:09, 2.69it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:08, 2.99it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:07, 3.24it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.40it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.54it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.68it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.79it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.88it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.78it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.86it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.93it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.96it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:03, 4.00it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.04it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.07it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.01it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 4.02it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.03it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.07it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.05it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 4.04it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.04it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.04it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.03it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.06it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.05it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.65it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.07it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.03it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.05it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.08it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.06it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:51, 1.83it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:42, 2.19it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:36, 2.54it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:31, 2.86it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:31, 2.90it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:28, 3.08it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:04<00:26, 3.28it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:25, 3.42it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:24, 3.49it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:23, 3.57it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.67it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.73it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.78it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.77it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.77it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.79it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.78it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.83it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.83it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.82it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.77it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.81it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.82it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.63it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.70it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.79it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.79it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.83it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.82it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.84it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.83it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.84it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.87it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.93it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.96it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:12<00:31, 1.89it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:25, 2.25it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:13<00:21, 2.59it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:13<00:19, 2.90it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:13<00:17, 3.18it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:15, 3.40it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.58it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:14<00:14, 3.69it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:14<00:13, 3.77it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.85it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.84it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.87it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.90it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.87it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.82it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.83it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.87it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.90it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.91it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.01it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.04it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.02it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:18<00:09, 4.04it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.97it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.91it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.90it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.85it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.87it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.83it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.82it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.81it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.85it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.84it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.85it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.84it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:22<00:13, 1.81it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:22<00:10, 2.15it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:08, 2.49it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:23<00:07, 2.80it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:23<00:06, 3.05it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:23<00:05, 3.24it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:23<00:05, 3.45it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.54it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.45it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.61it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.72it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.75it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.81it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.85it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.91it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.92it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.96it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.98it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.93it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.85it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.69it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.76it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.81it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.84it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.86it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.49it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.95it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.99it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.91it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.87it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.88it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.83it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.81it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.86it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:49, 1.83it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:41, 2.18it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:35, 2.52it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:04<00:31, 2.82it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:27, 3.13it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:26, 3.24it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:25, 3.37it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:05<00:24, 3.48it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:23, 3.58it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.64it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.70it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.77it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.84it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.84it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.86it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.89it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.91it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.88it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.94it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.77it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.52it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.55it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.67it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.71it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.74it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.79it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.84it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.81it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.87it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.84it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.83it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.88it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.91it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.82it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.70it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:13<00:31, 1.79it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:13<00:25, 2.14it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:21, 2.46it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:14<00:19, 2.76it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:14<00:17, 3.03it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:14<00:15, 3.26it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:14, 3.45it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:15<00:13, 3.58it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:15<00:13, 3.66it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.72it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.79it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.91it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.92it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.92it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.90it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.87it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.89it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.95it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.97it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.98it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.96it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.92it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.89it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.92it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.84it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.78it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.79it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.83it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.86it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.90it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.83it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.63it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.65it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.67it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.72it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:23<00:11, 1.86it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:23<00:09, 2.20it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:23<00:07, 2.55it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:24<00:06, 2.85it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:24<00:05, 3.11it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.29it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.46it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.59it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.72it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.80it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.81it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.84it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.87it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.90it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.86it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.82it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.82it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.78it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.80it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.78it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.81it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.84it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.47it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:26, 3.68it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:26, 3.67it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.76it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.76it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.77it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.74it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.77it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.76it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.75it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.73it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.74it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.75it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.78it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:47, 1.80it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:40, 2.09it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:05<00:35, 2.38it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:31, 2.63it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:28, 2.87it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:06<00:26, 3.10it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:24, 3.28it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:23, 3.40it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:22, 3.51it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:07<00:21, 3.60it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.65it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.72it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.79it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.78it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.80it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.81it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.78it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.82it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.82it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.82it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:10<00:18, 3.50it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:18, 3.54it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.61it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.69it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.68it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.68it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.71it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.74it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.73it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.74it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.72it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.75it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.82it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.90it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:14<00:27, 1.88it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:14<00:22, 2.23it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:15<00:19, 2.57it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:15<00:17, 2.88it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:15<00:15, 3.16it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:15<00:13, 3.36it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:16<00:13, 3.47it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.60it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.68it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:17<00:11, 3.72it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:17<00:11, 3.73it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.74it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.70it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.77it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.76it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.75it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.75it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.72it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.77it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.79it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.80it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.76it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.77it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.77it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.73it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:21<00:07, 3.71it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.74it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.76it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:22<00:06, 3.79it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.84it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.91it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.95it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:23<00:05, 3.92it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.97it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.99it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:24<00:09, 1.83it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:25<00:07, 2.16it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:25<00:06, 2.47it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:25<00:05, 2.77it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:25<00:04, 2.91it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:26<00:03, 3.10it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:26<00:03, 3.28it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.41it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.51it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:27<00:02, 3.57it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.63it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.72it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:28<00:01, 3.76it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:28<00:01, 3.73it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.72it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.75it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:29<00:00, 3.78it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:29<00:00, 3.81it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:29<00:00, 3.41it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:26, 3.76it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:26, 3.77it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.88it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.81it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.81it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.76it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.80it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.80it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.76it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.77it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.77it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.82it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.78it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:25, 3.34it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:25, 3.31it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:24, 3.45it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:48, 1.73it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:41, 1.98it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:06<00:35, 2.27it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:31, 2.56it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:27, 2.83it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:07<00:25, 3.05it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:07<00:23, 3.26it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:22, 3.38it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:21, 3.49it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.62it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.72it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.71it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.69it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.70it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.74it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.78it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.77it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.74it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.74it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.79it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.78it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.77it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.78it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.85it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.92it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.94it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.88it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.88it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.84it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.82it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.80it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.87it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.93it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.96it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.97it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:15<00:25, 1.87it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:16<00:21, 2.21it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:16<00:18, 2.54it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:16<00:15, 2.84it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:14, 3.09it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:17<00:13, 3.24it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:17<00:12, 3.35it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:17<00:11, 3.50it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.67it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.78it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.81it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.87it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.94it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.87it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.87it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.92it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.95it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.98it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.95it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.94it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.92it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.89it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.86it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.90it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.88it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.89it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.83it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.86it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.86it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.86it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.82it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.80it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.85it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.88it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.91it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:25<00:07, 1.86it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:25<00:05, 2.20it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:26<00:04, 2.54it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:26<00:03, 2.73it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.03it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:27<00:02, 3.23it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:27<00:02, 3.38it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.52it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.61it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:28<00:01, 3.66it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.67it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.71it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.67it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:29<00:00, 3.74it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:29<00:00, 3.43it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.87it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.99it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.96it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.92it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.87it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.91it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.93it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.90it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.93it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.95it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.92it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.91it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.95it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.94it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.96it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.87it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.90it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:20, 3.91it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:20, 3.97it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.97it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:44, 1.78it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:37, 2.09it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:31, 2.43it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:27, 2.75it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:25, 2.99it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:25, 2.91it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:08<00:24, 2.99it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:22, 3.18it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:21, 3.36it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.51it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.64it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.72it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.79it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.84it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.88it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.88it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.92it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.90it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.90it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.95it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.91it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.88it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.90it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.91it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.71it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.77it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.86it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.92it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.94it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.85it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:13, 3.69it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.73it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.74it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.73it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.75it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:23, 1.85it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:16<00:19, 2.21it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:17<00:16, 2.54it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:17<00:14, 2.83it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:12, 3.12it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:11, 3.37it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.53it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.66it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.75it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.78it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.76it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.59it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.38it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.49it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.62it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.68it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.82it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.91it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.99it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.96it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.88it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.83it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.69it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.79it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.85it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.87it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.85it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.82it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.84it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.78it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.84it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.88it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.91it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.95it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.91it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:26<00:04, 1.85it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:26<00:03, 2.20it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:27<00:02, 2.54it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:27<00:02, 2.85it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.12it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.35it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.54it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.69it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.78it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.84it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.47it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.09it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.06it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.10it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.05it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.01it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.98it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.97it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.97it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.95it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.97it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.99it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.03it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.03it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.02it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.05it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.01it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.78it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.76it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.75it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.78it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.80it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.87it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:19, 3.90it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.92it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.95it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:42, 1.74it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:35, 2.08it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:29, 2.41it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:25, 2.74it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:23, 3.04it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.29it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:19, 3.50it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.65it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.78it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.89it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.92it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.90it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.90it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.93it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.93it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.96it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.99it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.95it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.97it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.00it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.03it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.03it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.06it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.02it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.04it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.01it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.02it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.98it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.00it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.02it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.99it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.95it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.85it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.91it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.97it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:21, 1.85it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:17, 2.20it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:14, 2.54it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:12, 2.82it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:11, 3.08it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.33it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.52it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.69it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.77it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.85it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.89it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.92it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.85it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.86it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.92it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.90it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.91it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.96it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.01it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.03it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.01it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.94it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.96it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.98it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.97it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.98it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.88it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.75it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.78it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.83it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.89it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.86it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.85it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.89it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.96it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:27<00:02, 1.85it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:27<00:01, 2.20it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:27<00:00, 2.54it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 2.85it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.09it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.54it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.85it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:28, 3.42it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:30, 3.13it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:28, 3.40it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:26, 3.56it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.68it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.80it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.89it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.92it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.90it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.94it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.98it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.00it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.02it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.02it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.06it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.07it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.04it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.07it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.06it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.07it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.06it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:19, 3.99it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.93it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.78it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.79it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.81it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.85it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.80it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:38, 1.84it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:31, 2.17it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:27, 2.50it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:23, 2.80it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:21, 3.06it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:19, 3.30it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:18, 3.50it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.65it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.77it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.88it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.93it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.94it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.97it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.01it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.05it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.05it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.08it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.09it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.12it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.11it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.09it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.10it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.11it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.12it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.12it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.12it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.10it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.07it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.09it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.08it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.11it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.09it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.10it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.04it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.11it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.10it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:17, 1.90it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:14, 2.25it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:12, 2.59it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:10, 2.90it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:09, 3.18it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.40it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.56it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.67it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.76it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.80it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.53it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.55it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.62it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.68it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.78it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.86it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.87it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.90it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.91it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.96it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.97it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.99it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.94it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.86it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.84it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.82it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.87it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.91it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.90it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.93it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.98it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.04it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.01it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.99it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.98it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.68it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.97it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.05it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.06it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.04it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.01it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.01it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.01it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.03it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.05it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.06it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.10it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.12it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.10it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.11it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.07it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.07it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.92it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.90it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.69it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.79it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.85it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.87it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:19, 3.91it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.98it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.02it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.05it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.07it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.10it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.10it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.06it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.03it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.05it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.07it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.06it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:34, 1.89it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:28, 2.26it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:24, 2.57it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:21, 2.83it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:19, 3.08it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:18, 3.30it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:17, 3.44it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.61it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.73it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.68it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:17, 3.16it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:16, 3.34it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.52it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.67it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.74it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.80it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.86it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.89it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.89it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.89it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.88it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.87it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.83it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.82it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.81it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.83it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.82it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.84it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.84it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.86it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.69it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.75it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.82it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.85it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.85it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:16, 1.79it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:13, 2.16it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:11, 2.49it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:09, 2.81it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.04it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:07, 3.22it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:07, 3.26it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.46it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.63it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.72it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.79it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.89it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.96it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:23<00:04, 4.01it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.05it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.08it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.08it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:03, 4.07it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.04it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.04it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.04it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 4.04it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.05it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.95it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.97it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 4.01it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.01it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.04it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.05it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.04it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.04it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.65it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.92it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:28, 3.46it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:27, 3.54it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:26, 3.64it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.71it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:58, 1.61it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:46, 1.98it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:03<00:39, 2.33it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:37, 2.43it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:32, 2.77it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:04<00:29, 3.04it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:04<00:26, 3.26it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:25, 3.44it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:24, 3.53it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:05<00:23, 3.61it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.66it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.68it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.74it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.79it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.78it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.75it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.80it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.82it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.86it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.89it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.63it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.61it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.68it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.74it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.78it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.83it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.84it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.83it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.84it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.82it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.85it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.87it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.87it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.89it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.90it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.88it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:13<00:33, 1.72it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:13<00:27, 2.07it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:13<00:23, 2.40it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:14<00:20, 2.74it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:14<00:17, 3.01it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:14<00:16, 3.23it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:14<00:15, 3.42it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:15<00:14, 3.58it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:15<00:13, 3.72it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.79it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.88it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.91it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.93it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.92it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.93it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.95it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.99it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.96it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:10, 4.00it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:18<00:09, 4.04it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:18<00:09, 4.01it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.98it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.98it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.99it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.97it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.96it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.92it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.92it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.91it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.91it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.90it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.91it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.90it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.91it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.94it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.97it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:23<00:12, 1.83it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:23<00:09, 2.19it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:23<00:08, 2.50it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:24<00:06, 2.80it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:24<00:05, 3.08it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:24<00:05, 3.28it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:24<00:04, 3.49it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:25<00:04, 3.65it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.76it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.84it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.91it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.97it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:26<00:02, 4.00it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.98it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.96it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.97it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:27<00:01, 4.01it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:27<00:01, 4.01it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.04it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:28<00:00, 4.00it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:28<00:00, 4.02it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:28<00:00, 4.04it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 4.05it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.47it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.07it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.93it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:24, 3.95it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.95it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.97it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.95it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.93it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.92it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.92it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.86it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.90it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:04<00:47, 1.83it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:39, 2.20it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:33, 2.55it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:29, 2.84it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:05<00:27, 3.11it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:24, 3.35it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:23, 3.50it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.67it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.76it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.86it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.87it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.93it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.93it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.93it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.93it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.95it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.96it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.98it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.96it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.00it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.03it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.03it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.00it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.01it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.99it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.00it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.98it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.98it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.02it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.00it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.96it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.96it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.00it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.97it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.94it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.95it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:14<00:29, 1.74it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:14<00:24, 2.09it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:20, 2.43it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:17, 2.76it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:15<00:15, 3.05it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:15<00:14, 3.30it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:13, 3.48it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.62it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.77it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.84it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.86it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.90it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.97it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.02it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.01it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.04it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.07it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.08it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.05it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.02it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.97it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.01it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.98it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.00it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.05it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.05it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.01it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.05it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.04it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.04it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.01it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.03it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.05it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.08it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.00it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.03it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.01it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:24<00:08, 1.82it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:24<00:06, 2.18it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:05, 2.53it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:25<00:04, 2.85it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.13it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:25<00:03, 3.28it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.42it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:26<00:02, 3.52it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.67it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.75it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.86it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:27<00:01, 3.93it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.97it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.92it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.92it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.93it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:28<00:00, 3.56it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:27, 3.57it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:28, 3.49it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:26, 3.63it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:26, 3.68it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:25, 3.75it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:24, 3.83it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.89it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.91it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.94it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.92it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.92it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.91it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.94it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.95it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.91it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.88it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.87it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:20, 3.92it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:20, 3.93it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:06<00:43, 1.83it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:36, 2.19it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:30, 2.55it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:27, 2.85it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:07<00:24, 3.12it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:22, 3.35it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:21, 3.52it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.65it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.77it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.87it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.93it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.96it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.01it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.05it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.06it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.07it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.07it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.11it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.09it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.09it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.09it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.10it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.12it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.12it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.10it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.09it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.10it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.10it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.90it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.81it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.86it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.91it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.94it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.90it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.92it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.96it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:16<00:24, 1.78it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:16<00:20, 2.13it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:16, 2.49it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:14, 2.79it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:17<00:13, 3.05it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:17<00:11, 3.29it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.49it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.63it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.68it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.75it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.84it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.90it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.94it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.99it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.03it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.05it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.05it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.07it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.08it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.05it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.05it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.07it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.08it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.09it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.06it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.07it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.08it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.07it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.03it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.05it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.06it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.04it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.05it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.07it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.07it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.09it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:26<00:04, 1.85it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:26<00:03, 2.21it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:26<00:02, 2.57it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 2.88it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:01, 3.16it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.39it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.60it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.74it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.84it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.58it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.16it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.11it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.10it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.13it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.11it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.10it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.08it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.86it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.76it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.73it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.82it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.87it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.94it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.98it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.02it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.07it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.09it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.10it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.10it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.11it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.12it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.12it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.10it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.06it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.07it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:39, 1.85it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:32, 2.23it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:28, 2.55it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:24, 2.89it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:22, 3.18it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.43it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.57it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.72it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.83it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.92it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.95it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.00it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.03it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.06it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.03it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.03it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.02it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.04it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.04it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.06it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.05it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.05it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.02it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.04it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.01it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.04it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.04it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.10it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.95it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.97it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.97it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.99it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.01it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.02it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.01it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.97it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.00it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:20, 1.81it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:16, 2.16it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:18<00:13, 2.51it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:11, 2.84it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:10, 3.08it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.25it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.45it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.61it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.74it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.84it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.91it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.93it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.93it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.98it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.97it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.95it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.92it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.91it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.94it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.96it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.00it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.99it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.02it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.03it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.05it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.04it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.06it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.02it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.89it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.86it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.89it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.87it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.90it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.90it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.92it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.96it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:27<00:00, 1.80it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 2.15it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.58it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.05it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.00it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.02it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.01it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.99it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.97it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:23, 3.98it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.99it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.02it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.06it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:22, 3.97it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.92it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.97it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:21, 3.98it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.80it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:23, 3.64it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:22, 3.68it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.77it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.84it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.88it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.92it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.89it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:19, 3.94it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.92it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 3.95it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:18, 3.93it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:18, 3.95it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.99it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.02it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.00it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.03it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.04it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.05it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:36, 1.83it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:29, 2.21it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:10<00:24, 2.59it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:21, 2.93it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:19, 3.24it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.50it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.70it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.81it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.90it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.96it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.01it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.04it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.08it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.08it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.07it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.12it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.16it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.17it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.20it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.23it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.13it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.07it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.93it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.97it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.99it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.98it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.00it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.06it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.02it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.97it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.96it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.01it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.99it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.03it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.01it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:16, 1.79it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:13, 2.15it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:11, 2.48it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:20<00:09, 2.80it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:20<00:08, 3.06it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.26it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.44it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:21<00:06, 3.60it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.72it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.81it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.90it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.96it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.00it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.02it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.05it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.12it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.09it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.06it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.87it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.96it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.04it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.09it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.12it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.17it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.22it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.25it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.25it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.22it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.19it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.19it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.19it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.73it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:25, 3.92it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.04it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.07it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.05it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.06it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:54, 1.73it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:43, 2.13it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:36, 2.53it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:31, 2.87it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:28, 3.17it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:26, 3.42it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:24, 3.62it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:23, 3.76it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:22, 3.88it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.97it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.01it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:20, 4.05it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.11it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.13it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.12it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.12it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.11it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.06it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.87it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.87it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.99it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.11it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.12it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.18it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.23it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.25it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.21it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.17it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.16it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.15it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.14it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.11it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.09it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.08it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.08it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.09it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:12<00:29, 1.94it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:24, 2.33it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:20, 2.69it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:18, 3.05it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:13<00:16, 3.34it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.54it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.68it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.81it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.90it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.97it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.02it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.04it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.11it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.13it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.14it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.14it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.14it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.12it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.14it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.14it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.14it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.16it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.14it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.13it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.14it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.13it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.15it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.15it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.16it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.23it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.21it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.19it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.18it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.17it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.17it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:11, 1.87it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:09, 2.23it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:22<00:07, 2.57it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:06, 2.89it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.19it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.43it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.63it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.77it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.87it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.97it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.01it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.06it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.07it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.10it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.12it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.13it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.13it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.15it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.17it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.14it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.14it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.13it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.12it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.70it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.12it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.16it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.14it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.14it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.16it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.11it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.06it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.06it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.10it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:47, 1.84it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:39, 2.22it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:33, 2.58it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:29, 2.91it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:26, 3.21it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:24, 3.43it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.62it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.77it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.87it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.96it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.01it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.06it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.08it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.07it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.08it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.10it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.13it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.14it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.13it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.14it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.13it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.14it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.15it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.94it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.86it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.89it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.98it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.97it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.01it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.03it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.06it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.09it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.11it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.15it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.14it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:27, 1.88it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:22, 2.24it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:19, 2.61it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:16, 2.94it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:14, 3.22it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:13, 3.46it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.64it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.75it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.84it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.90it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.96it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:10, 4.01it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.04it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.06it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.08it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.09it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.11it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.11it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.13it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.13it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.14it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.14it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.15it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.15it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.18it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.16it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.16it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.15it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.15it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.14it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.14it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.12it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.12it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:08, 1.85it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:06, 2.22it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:05, 2.58it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:04, 2.91it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.19it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.44it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.57it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.69it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.81it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.91it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.98it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:26<00:01, 4.04it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.07it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.10it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.11it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.13it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.12it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.67it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.12it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.15it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.12it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.17it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.15it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.15it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.14it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.14it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.14it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.14it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.14it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.15it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.16it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.15it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.15it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.14it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.14it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:42, 1.86it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:35, 2.22it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:29, 2.58it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:26, 2.91it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:23, 3.20it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:21, 3.42it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.61it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.76it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.83it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.91it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.97it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.00it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.05it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.08it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.09it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.09it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.12it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.12it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.13it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.15it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.13it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.12it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.14it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.03it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.99it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.06it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.05it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.11it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.18it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.24it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.29it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.29it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.31it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.33it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.34it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:22, 1.95it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:18, 2.31it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:15, 2.66it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:13, 2.98it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.27it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.48it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.67it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.82it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.91it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.94it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.99it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.05it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.08it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.09it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.11it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.07it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.09it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.10it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.11it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.12it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.13it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.13it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.13it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.12it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.13it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.14it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.14it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.13it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.13it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.12it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.14it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.15it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.14it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.15it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.14it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.13it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:03, 1.85it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:02, 2.22it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 2.57it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:01, 2.90it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.18it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.42it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.61it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.78it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.70it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.20it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.12it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.11it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.09it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.09it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.10it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.12it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.12it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.12it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.11it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.12it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.13it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.13it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.13it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.14it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.14it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.15it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.17it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.13it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.13it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.13it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.13it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.12it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.14it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.14it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.15it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:39, 1.85it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:32, 2.22it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:27, 2.59it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:23, 2.92it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:21, 3.20it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.43it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.61it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.77it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.87it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.95it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.00it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.04it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.07it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.10it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.11it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.11it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.20it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.17it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.16it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.15it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.14it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.14it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.13it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.13it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.12it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.13it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.16it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.09it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.09it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.01it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.06it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.05it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.12it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.18it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.20it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.17it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.21it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:18, 1.88it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:15, 2.25it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:12, 2.64it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:10, 2.98it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.28it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.49it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.65it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.80it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.90it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.96it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.01it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.05it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.05it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.10it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.11it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.15it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.20it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.19it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.21it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.22it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.18it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.16it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.16it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.17it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.16it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.16it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.16it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.16it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.15it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.14it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.15it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.15it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.15it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.12it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.13it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.15it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.84it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.08it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.09it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.12it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.14it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.12it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.09it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.02it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.05it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.04it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.11it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.16it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.15it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.15it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.14it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.14it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.13it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.14it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.13it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.14it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.11it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.11it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.13it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.15it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.14it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.14it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.15it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.15it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.14it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.15it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.15it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.14it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.14it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:34, 1.85it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:28, 2.22it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:24, 2.58it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:20, 2.91it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:18, 3.20it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.44it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.63it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.79it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.88it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 3.94it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.03it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.13it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.18it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.23it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.23it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.15it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.14it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.16it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.16it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.14it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.15it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.14it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.14it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.14it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.15it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.14it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.15it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.14it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.15it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.15it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.16it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.17it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.18it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.16it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.16it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:14, 1.84it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:11, 2.21it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:09, 2.58it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:08, 2.90it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.19it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.47it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.67it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.79it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 3.89it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 3.95it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.02it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.06it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.07it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.11it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.11it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.10it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.11it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.12it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.14it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.16it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.15it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.12it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.14it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.14it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.14it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.15it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.17it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.15it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.83it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.11it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.16it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.12it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.12it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.12it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:49, 1.81it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:40, 2.18it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:34, 2.55it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:30, 2.89it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:26, 3.19it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:24, 3.42it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:23, 3.61it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.76it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.87it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.95it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.98it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.98it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.04it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.06it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.12it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.17it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.17it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.15it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.14it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.14it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.13it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.14it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.13it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.13it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.11it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.13it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.10it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.09it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.08it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.09it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.10it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.13it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.13it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.14it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.13it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:28, 1.84it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:23, 2.21it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:19, 2.57it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:14<00:17, 2.90it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:15, 3.19it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:14, 3.43it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.63it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.77it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.88it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.95it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.01it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:16<00:10, 4.03it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:10, 4.05it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.08it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.10it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:17<00:09, 4.11it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.12it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.14it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.15it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.16it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.15it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.13it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.14it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.15it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.14it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.13it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.12it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.14it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.14it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.13it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.14it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.16it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.16it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.15it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.15it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:23<00:08, 1.84it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:23<00:06, 2.21it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:05, 2.57it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:24<00:04, 2.91it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.22it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:24<00:03, 3.49it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.66it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.80it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.89it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.96it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.02it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.08it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.08it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.09it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.08it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.10it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 4.11it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.68it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.06it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.14it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.11it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.06it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.06it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.10it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.11it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.12it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:22, 4.11it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.12it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.13it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.13it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.13it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.13it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.13it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.14it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.14it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.14it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.13it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:43, 1.84it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:35, 2.21it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:30, 2.57it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:26, 2.89it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:23, 3.18it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:21, 3.42it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.60it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:19, 3.75it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.85it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.94it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.99it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.01it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.02it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.09it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:16, 4.10it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.15it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.19it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.20it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.16it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.15it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.14it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.16it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.15it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.14it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.11it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.14it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.21it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.18it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.21it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.27it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.24it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.22it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.21it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.20it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.19it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.17it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.16it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:23, 1.84it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:19, 2.21it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:15, 2.58it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:13, 2.91it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.19it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.43it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.62it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.76it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.87it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.94it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:08, 4.00it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.04it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.07it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.09it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.11it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.09it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.10it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.11it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 4.13it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.15it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.16it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.14it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.15it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.15it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.15it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.15it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.16it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.13it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.14it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.18it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.25it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.28it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.31it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.28it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.25it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.24it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.18it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:03, 1.84it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:02, 2.21it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:01, 2.57it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:01, 2.91it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.20it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.46it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.68it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:27<00:00, 3.69it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.32it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.33it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.31it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.33it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.33it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.34it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.35it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.30it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.32it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.33it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.34it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.35it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.36it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.39it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.35it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.33it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.27it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.23it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.21it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.19it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.16it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.18it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.15it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.15it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.14it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.14it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.14it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:39, 1.83it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:32, 2.20it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:27, 2.56it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:23, 2.89it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:21, 3.19it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.43it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.61it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.76it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.89it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 3.95it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.99it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.03it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.06it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.09it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.12it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.07it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.07it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.08it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.14it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.20it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.21it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.18it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.17it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.17it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.17it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.19it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.19it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.17it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.14it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.14it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.15it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.14it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.14it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.12it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.12it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.14it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:18, 1.84it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:14, 2.21it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:12, 2.57it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:10, 2.90it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:09, 3.18it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.41it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.60it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.76it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.87it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.94it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.97it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.02it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.99it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.05it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.13it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.20it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.26it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.27it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.29it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.31it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.32it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.34it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.36it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.30it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.24it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.22it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.20it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.20it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.17it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.15it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.11it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.12it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.12it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.13it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.13it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.86it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:01<02:03, 1.24s/it]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<01:03, 1.54it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:44, 2.18it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:35, 2.71it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:30, 3.14it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:27, 3.48it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:25, 3.70it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.83it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.92it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:22, 4.03it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.08it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.10it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.11it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.12it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.20it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.26it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.32it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.36it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.40it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.39it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.38it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.39it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.39it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.38it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.41it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.43it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.45it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.43it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.40it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.44it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.48it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.49it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.50it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.49it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.50it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.49it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.49it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:31, 1.95it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:26, 2.34it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:22, 2.72it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:19, 3.08it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:17, 3.41it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:15, 3.65it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.86it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.02it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.14it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.22it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.29it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.33it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.38it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.36it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.35it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.37it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.40it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.40it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.39it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.40it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.39it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.37it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.36it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.37it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.39it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.41it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.42it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.41it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.43it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.43it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.43it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.41it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.42it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.42it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.41it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.40it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.40it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:12, 1.94it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:10, 2.32it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:08, 2.71it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:07, 3.06it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.38it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.63it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 3.83it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 3.99it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.11it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.21it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.30it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.35it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.36it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.39it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.41it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.41it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.41it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.41it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.42it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.41it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.42it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.42it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.42it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.44it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.46it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.44it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.90it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.37it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.37it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.39it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.37it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.39it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.39it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.40it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.40it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.40it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:46, 1.91it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:37, 2.31it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:32, 2.64it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:28, 2.97it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:25, 3.23it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:23, 3.49it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.70it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:21, 3.86it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.00it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.13it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.22it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.28it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.34it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.33it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.37it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.40it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.40it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.40it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.41it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.44it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.43it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.43it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.41it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.41it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.42it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.41it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.37it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.38it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.41it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.41it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.42it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.42it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.43it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.43it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.45it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.43it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.42it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:26, 1.94it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:21, 2.33it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:18, 2.71it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:15, 3.06it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:13, 3.37it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.63it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.85it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.99it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.10it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.20it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.24it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.30it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.33it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.37it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.38it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.42it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.43it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.44it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.43it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.42it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.42it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.41it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.42it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.43it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.44it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.42it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.42it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.40it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.38it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.41it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.39it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.39it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.40it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:03, 4.40it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.42it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.43it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:07, 1.94it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:05, 2.33it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:04, 2.72it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.08it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.40it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.66it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.86it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.01it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.12it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.23it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.30it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.35it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.37it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.38it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.40it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.90it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.43it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.41it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.43it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.42it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.42it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.40it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.43it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.39it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.41it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.40it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.42it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.41it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.41it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.41it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.43it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.40it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:40, 1.92it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:33, 2.32it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:28, 2.70it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:26, 2.86it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:27, 2.71it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:24, 2.97it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:23, 3.09it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:23, 2.99it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:23, 3.03it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:21, 3.25it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.41it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.61it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.76it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.90it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.01it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.03it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.11it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.16it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.23it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.22it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.24it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.31it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.34it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.31it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.30it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.32it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.32it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.26it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.26it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.28it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.31it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.28it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.25it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.29it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.26it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.30it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.33it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:21, 1.87it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:17, 2.26it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:14, 2.66it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.01it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:11, 3.34it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.61it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.81it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.98it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.11it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.21it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.29it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.36it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.40it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.41it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.42it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.43it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.36it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.37it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.36it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.38it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.38it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.39it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.40it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.42it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.38it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.34it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.36it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.38it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.39it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.40it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.41it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.41it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.40it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.40it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.41it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.30it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:02, 1.85it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:01, 2.23it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 2.61it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 2.96it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.29it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.77it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.36it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.38it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.40it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.38it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.37it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.37it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.39it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.34it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.34it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.35it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.37it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.37it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.39it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.38it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.38it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.40it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.43it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.41it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.39it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.38it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.37it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.36it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.37it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.37it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.39it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:06<00:15, 4.40it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:36, 1.91it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:29, 2.31it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:24, 2.68it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:21, 3.02it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.30it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.54it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.74it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:15, 3.89it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.02it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.97it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.05it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.13it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.10it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.18it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.16it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.04it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.09it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.11it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.20it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.27it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.32it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.36it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.33it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.34it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.36it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.40it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.40it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.40it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.40it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.43it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.42it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.42it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.40it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.41it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:15<00:07, 4.43it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.42it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.42it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.43it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:16<00:06, 4.43it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:15, 1.90it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:12, 2.29it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:10, 2.66it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.02it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.32it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.55it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.74it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 3.90it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.05it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.16it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.23it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.28it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.32it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.33it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.36it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.38it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.37it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.35it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.33it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.35it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.35it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.38it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.38it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.40it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.39it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 3.54it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:01, 3.75it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 3.93it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.07it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.18it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.25it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.98it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.41it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.42it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.41it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.42it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:58, 1.62it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:45, 2.06it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:37, 2.50it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:31, 2.89it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:28, 3.22it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:25, 3.51it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.75it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.95it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.09it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.18it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.22it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.24it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.30it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.32it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.36it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.39it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.37it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.37it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.39it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.42it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.41it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.38it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.38it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.40it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.39it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.41it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.39it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.41it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.41it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.40it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.41it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.42it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.43it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.41it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.43it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.44it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.40it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:30, 1.90it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:25, 2.28it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:21, 2.66it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:18, 3.01it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:16, 3.33it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.59it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.79it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.94it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.06it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.15it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.24it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.29it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.32it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.33it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.32it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.35it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.36it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.38it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.39it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.41it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.40it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.38it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.37it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.38it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.40it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.42it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.40it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.36it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.35it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.37it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.38it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.29it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.32it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.34it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.37it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.38it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.39it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.36it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:09, 1.90it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:07, 2.28it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:06, 2.67it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.02it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.33it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 3.59it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 3.80it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.93it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.05it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.12it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.18it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.23it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.30it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.33it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.35it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.37it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.38it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.38it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.37it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.38it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.86it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.38it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.39it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.40it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.40it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.43it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.43it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.44it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.40it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.35it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.29it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.28it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.25it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:45, 1.86it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:37, 2.22it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:31, 2.56it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:27, 2.91it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:24, 3.20it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.49it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.74it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.93it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.08it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.18it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.26it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.33it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.37it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.38it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.38it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.37it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.35it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.36it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.38it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.38it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.39it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.35it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.34it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.37it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.40it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.40it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.39it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.40it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.39it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.35it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.35it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.38it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.37it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.40it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.41it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.40it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.39it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:24, 1.90it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:20, 2.30it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:16, 2.68it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:14, 3.04it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.35it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.62it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.80it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:10, 3.92it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 3.99it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.08it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.14it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.18it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.25it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.30it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.18it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.21it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.27it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.32it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.34it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.33it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.34it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.37it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.41it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.43it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.45it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.46it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.37it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.34it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.29it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.25it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.21it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.19it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.19it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.18it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.16it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.14it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.13it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.14it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.18it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:04, 1.86it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:03, 2.24it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:02, 2.62it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 2.98it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.31it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.57it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.75it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.89it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.00it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.83it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.35it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.36it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.39it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.40it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.40it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.40it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.38it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.31it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.27it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.28it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.29it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.33it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.37it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.40it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.39it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.39it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.39it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.37it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.37it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.33it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.36it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.38it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.36it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:38, 1.89it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:31, 2.28it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:26, 2.65it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:23, 3.02it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:20, 3.33it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.60it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.81it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:16, 3.98it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.10it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.17it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.24it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.26it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.29it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.32it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.36it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.38it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.39it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.40it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.40it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.20it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.17it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.11it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.14it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.19it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.25it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.31it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.33it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.36it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.34it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.37it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.37it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.36it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.32it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.31it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.32it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.33it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.33it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:19, 1.88it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:15, 2.27it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:12, 2.65it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.02it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.33it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.60it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 3.79it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:07, 3.95it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.06it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.15it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.20it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.25it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.27it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.31it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.33it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.34it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.37it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.38it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.36it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.34it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.33it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.35it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.37it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.34it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.31it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.31it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.31it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.33it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.32it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.33it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.33it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.32it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.31it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.32it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.35it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.38it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.39it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.00it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:01<02:07, 1.29s/it]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<01:06, 1.48it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:46, 2.08it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:02<00:36, 2.62it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:31, 3.06it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:27, 3.40it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:25, 3.68it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.82it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.93it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:22, 4.04it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.14it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.18it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.18it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.14it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.17it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.22it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.25it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.28it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.34it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.32it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.32it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.29it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.29it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.32it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.33it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.33it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.31it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.32it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.35it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.35it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.39it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.38it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.35it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.37it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.36it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.35it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.31it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.34it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:11<00:32, 1.86it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:26, 2.24it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:22, 2.62it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:19, 2.96it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:12<00:17, 3.24it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.51it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.72it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.89it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.98it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.10it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.15it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.15it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.19it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.20it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.27it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.32it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.32it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.30it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.29it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.28it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.27it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.25it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.26it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.25it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.22it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.25it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.24it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.24it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.26it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.21it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.21it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.25it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.25it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.27it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.23it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.24it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.26it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.28it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.26it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:21<00:12, 1.82it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:09, 2.21it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:07, 2.58it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:22<00:06, 2.91it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.23it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.51it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.73it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 3.91it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.05it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.16it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.25it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.26it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.23it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.25it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.27it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.30it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.27it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.29it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.28it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.25it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.26it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.28it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.29it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.78it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.13it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.16it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.16it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.20it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.17it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.19it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.22it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.18it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.18it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.15it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.11it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.19it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.14it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:48, 1.78it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:39, 2.13it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:33, 2.48it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:29, 2.82it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:26, 3.13it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:23, 3.39it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.61it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.72it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.87it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:19, 4.01it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.09it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.13it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.17it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.15it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.20it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.11it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.14it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.19it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.18it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.19it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.21it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.16it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.12it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.21it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.16it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.15it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.17it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.14it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.16it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.20it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.23it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.23it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.26it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.24it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.20it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.18it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.20it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:26, 1.82it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:21, 2.21it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:17, 2.60it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:15, 2.95it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:13, 3.25it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:12, 3.52it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:11, 3.75it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.88it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.04it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.12it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.18it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.18it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.26it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.32it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.34it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.37it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.39it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.38it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.39it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.41it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.42it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.41it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.41it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.36it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.37it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.39it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.40it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.42it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.42it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.40it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.39it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.41it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.42it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.40it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.39it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.40it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.42it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.41it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:04, 1.87it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:03, 2.25it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:02, 2.63it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:02, 3.00it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.32it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:01, 3.59it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.80it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.98it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.11it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.22it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.77it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.37it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.39it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.41it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.36it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.39it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.40it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.40it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.40it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.39it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.42it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.38it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.34it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.36it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.40it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.37it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.38it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.39it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.41it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.40it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.40it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.43it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:39, 1.89it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:31, 2.29it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:26, 2.68it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:23, 3.04it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:21, 3.26it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.49it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.63it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.82it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:16, 3.97it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.09it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.18it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.21it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.21it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.20it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.22it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.22it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.25it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.25it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.26it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.23it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.29it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.32it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.30it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.28it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.29it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.28it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.31it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.34it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.34it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.37it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.38it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.36it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.37it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.38it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.39it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.38it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.37it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.38it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.37it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:18, 1.87it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:15, 2.26it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:12, 2.64it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:10, 3.00it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.33it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.60it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:07, 3.82it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:07, 3.96it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.08it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.19it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.26it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.31it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.36it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.36it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.35it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.37it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.38it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.39it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.39it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.40it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.38it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.37it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.38it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.35it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.33it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.34it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.34it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.33it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.33it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.35it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.38it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.39it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.38it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.40it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.41it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.01it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:01<02:04, 1.25s/it]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:01<01:03, 1.54it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:01<00:44, 2.18it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:01<00:35, 2.73it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:29, 3.17it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:26, 3.50it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:24, 3.73it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:23, 3.91it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:22, 4.04it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:22, 4.08it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.09it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.16it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.23it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.28it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.33it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.35it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.40it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.37it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.33it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.34it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.35it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.38it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.39it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.40it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.39it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.39it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.38it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.41it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.43it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.43it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.41it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.39it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.36it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.37it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.39it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.43it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.45it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.43it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:32, 1.89it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:11<00:26, 2.28it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:11<00:22, 2.67it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:19, 3.02it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:17, 3.33it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:15, 3.57it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.75it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:14, 3.83it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 3.86it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.95it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.01it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.12it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.20it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.30it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.34it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.37it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.38it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.41it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.43it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.39it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.40it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.33it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.28it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.22it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.22it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.25it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.23it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.27it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.31it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.30it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.34it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.34it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.36it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.34it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.35it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.34it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.34it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.31it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.29it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.33it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:11, 1.85it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:08, 2.23it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:07, 2.61it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:06, 2.95it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:05, 3.26it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.53it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 3.75it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 3.92it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.03it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.15it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.19it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.17it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.23it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.28it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.33it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.35it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.36it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.36it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.38it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.39it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.37it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.38it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.84it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.28it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.30it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.34it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.35it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.37it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.17it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.17it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.19it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.26it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.30it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.31it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.34it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.32it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:45, 1.86it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:37, 2.23it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:31, 2.62it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:27, 2.98it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:24, 3.31it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:22, 3.59it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:20, 3.81it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.98it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.09it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.09it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.05it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.06it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:18, 4.03it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.06it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.09it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:17, 4.10it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.08it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.09it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.08it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.15it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.10it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.11it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.11it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.13it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.07it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.13it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.13it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.16it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.11it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.08it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:13, 4.05it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.08it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.08it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.06it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:12, 4.08it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.12it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.09it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.12it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:25, 1.79it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:20, 2.18it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:16, 2.55it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:14, 2.90it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.20it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.44it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.66it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.77it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.88it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.01it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.04it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.11it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.17it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.15it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.17it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:07, 4.12it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.17it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.22it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.20it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.23it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.22it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.22it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.17it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.20it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.16it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.19it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.20it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.16it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.19it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.19it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.20it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.21it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.21it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.21it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.20it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.14it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.12it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:25<00:03, 1.79it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:02, 2.15it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:02, 2.50it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:26<00:01, 2.86it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.18it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.43it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.60it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.77it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.70it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.12it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.21it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.16it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.19it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:23, 4.13it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.13it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.14it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.16it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.16it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.19it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:21, 4.15it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.12it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.12it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.14it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:20, 4.19it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.08it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.07it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.03it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.07it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.09it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.12it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.15it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.12it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.15it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.16it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.13it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:40, 1.77it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:08<00:33, 2.15it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:27, 2.51it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:24, 2.86it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:21, 3.15it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:09<00:19, 3.41it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.59it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:17, 3.74it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.87it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:10<00:16, 3.93it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.98it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:15, 4.02it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.09it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.08it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:11<00:14, 4.10it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.12it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.13it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.14it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.17it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.18it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.14it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.15it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.19it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.18it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.20it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.15it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.17it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.14it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.13it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.13it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.13it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.16it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.15it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.17it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.19it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.12it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.15it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.17it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.22it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.18it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:18, 1.77it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:14, 2.14it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:19<00:12, 2.49it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:19<00:10, 2.85it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:19<00:08, 3.13it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.41it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:07, 3.58it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.72it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:20<00:06, 3.86it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.94it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.99it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:21<00:05, 4.05it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.06it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.17it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.24it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:04, 4.19it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.14it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.17it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.20it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 4.24it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.24it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.24it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.21it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.22it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.17it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.18it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.19it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.20it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.16it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.17it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.17it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.21it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.22it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.82it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.28it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.25it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.18it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:02<01:03, 1.51it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:02<00:48, 1.97it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:38, 2.41it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:33, 2.81it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:29, 3.13it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:26, 3.41it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:24, 3.63it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.78it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:22, 3.91it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.99it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:21, 4.07it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.14it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.23it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.27it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.34it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.36it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.37it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.36it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.40it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.41it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.41it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.41it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.42it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.45it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.34it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.23it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.24it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.19it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.21it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.18it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.19it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.21it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.21it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.18it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.17it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.19it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.20it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.19it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.17it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.15it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:12<00:31, 1.80it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:12<00:25, 2.17it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:21, 2.54it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:13<00:18, 2.88it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:13<00:16, 3.19it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.44it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.62it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.80it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.89it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.02it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.09it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.11it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.15it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.14it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.17it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.17it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.21it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.20it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:09, 4.20it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.25it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.31it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.37it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.40it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.43it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.40it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.39it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.38it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.38it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.40it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:19<00:06, 4.42it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.42it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.40it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.38it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:20<00:05, 4.40it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.41it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.40it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.38it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:21<00:04, 4.39it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:22<00:09, 1.86it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:22<00:07, 2.25it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:06, 2.65it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:05, 2.98it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:23<00:04, 3.27it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.55it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.71it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.88it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:24<00:02, 3.94it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:24<00:02, 4.05it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.05it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.12it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.17it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:25<00:01, 4.18it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.15it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.16it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.15it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.16it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 4.19it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:26<00:00, 3.77it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:24, 4.11it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.13it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:23, 4.18it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.18it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.15it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.17it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.25it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.32it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.36it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.41it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.40it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.42it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.41it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.41it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.38it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:44, 1.87it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:36, 2.27it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:30, 2.66it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:26, 3.02it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:23, 3.35it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:21, 3.62it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.82it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.99it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.12it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.23it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.29it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.33it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.38it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.41it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.39it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.39it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.39it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.30it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.28it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.32it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.36it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.34it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.32it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.37it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.40it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.44it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.23it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.18it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.17it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.25it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.27it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.32it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.30it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.32it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.33it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.34it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.37it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.39it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.36it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.38it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:23, 1.85it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:18, 2.24it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:15, 2.62it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:13, 2.99it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.32it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.60it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.81it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.97it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.12it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.23it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.26it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.32it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.38it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.41it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.42it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.39it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.40it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.42it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.43it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.41it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.41it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.41it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.43it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.43it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.41it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.42it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.45it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.46it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.46it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.43it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.40it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.40it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.19it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.15it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.20it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.24it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.29it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.35it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:02, 1.88it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:25<00:01, 2.27it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:01, 2.64it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 2.99it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.32it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.59it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.85it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.42it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.44it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.41it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.43it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.45it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.44it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.43it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.47it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.36it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.35it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.37it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.40it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.42it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.43it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.41it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.41it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.45it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.45it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.42it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.43it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.41it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.42it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.44it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.44it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.41it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.37it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.33it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:37, 1.86it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:30, 2.26it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:25, 2.66it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:22, 3.02it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:19, 3.35it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:18, 3.61it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.84it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.01it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.15it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.25it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.33it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.39it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.37it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.41it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.39it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.40it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.43it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.45it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.45it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.42it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.45it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.47it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.41it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.40it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.41it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.44it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.43it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.45it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.45it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.46it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.38it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.28it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.26it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.23it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.26it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.28it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:15<00:07, 4.34it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.38it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.35it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.31it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:15, 1.88it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:12, 2.27it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:10, 2.65it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:08, 3.02it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:07, 3.36it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.63it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.86it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.00it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.10it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.21it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.27it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.33it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.38it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:03, 4.42it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.41it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.43it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.41it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.43it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.46it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.48it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.48it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.50it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:22<00:01, 4.49it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.49it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.49it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.47it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:23<00:00, 4.44it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:23<00:00, 4.42it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.43it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.45it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.47it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.06it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.38it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.42it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.34it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.40it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.42it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:02<00:54, 1.71it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:02<00:43, 2.15it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:02<00:35, 2.58it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:30, 2.97it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:27, 3.31it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:24, 3.60it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:23, 3.82it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:03<00:21, 4.00it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.13it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.25it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.24it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:19, 4.18it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.19it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.28it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.36it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.33it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.35it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.37it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.40it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.43it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.35it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.33it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.36it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.38it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.35it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.38it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.42it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.44it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.46it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.47it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.47it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.44it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.43it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.41it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.37it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.36it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.34it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.38it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.37it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.38it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:12<00:28, 1.88it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:12<00:23, 2.27it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:12<00:19, 2.66it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:16, 3.03it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:14, 3.36it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:13, 3.64it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:12, 3.85it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.95it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:11, 4.06it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.17it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.21it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:15<00:10, 4.30it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.34it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.38it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.37it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.41it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.41it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.43it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.39it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.42it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.42it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.38it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.37it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.41it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.43it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.43it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.45it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.42it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.41it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.42it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.42it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.44it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.46it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.42it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.36it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.36it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.36it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:03, 4.39it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:22<00:08, 1.87it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:22<00:06, 2.26it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:22<00:05, 2.66it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:04, 3.02it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.34it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.62it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.86it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.02it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.15it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.24it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.30it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.33it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.35it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.36it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.37it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.40it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.42it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.88it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.35it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.37it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.38it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.40it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.36it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.36it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.39it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.43it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.39it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.40it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.42it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.41it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.41it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.43it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.42it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.43it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.42it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:43, 1.88it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:35, 2.29it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:29, 2.67it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:05<00:25, 3.04it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:22, 3.37it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:20, 3.63it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:19, 3.85it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:18, 4.04it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.16it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:17, 4.21it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.25it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.31it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.36it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.40it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.42it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.38it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.27it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.25it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.23it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.24it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.30it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.33it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.34it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.35it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.39it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.43it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.42it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.42it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.44it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.45it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.38it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.37it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.41it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.40it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.41it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.39it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.41it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.40it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.40it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.42it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:21, 1.87it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:17, 2.26it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:14, 2.65it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:12, 3.00it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.32it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:10, 3.57it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:09, 3.79it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.96it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:08, 4.11it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.21it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.22it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.27it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.29it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.34it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.34it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.34it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.36it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.38it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.37it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.38it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.41it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.42it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.43it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:03, 4.44it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.44it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.46it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.44it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.39it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.40it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.42it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.39it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.38it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:22<00:01, 4.43it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.40it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.40it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.42it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:23<00:00, 4.42it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:01, 1.86it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 2.25it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 2.63it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 2.98it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.88it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.44it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.47it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.44it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.44it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.42it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.43it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.42it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.34it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.31it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.31it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.27it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.31it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.36it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.39it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.42it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.45it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.43it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.43it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.45it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.47it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.47it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.46it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.49it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.44it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.42it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.41it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.43it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:06<00:15, 4.44it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:06<00:15, 4.45it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.44it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.46it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.46it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:35, 1.87it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:28, 2.26it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:24, 2.64it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:20, 3.00it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:18, 3.34it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:16, 3.62it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:15, 3.81it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:14, 3.98it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:14, 4.12it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.22it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.28it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.33it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.37it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.34it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.29it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.33it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.35it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.38it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.16it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.17it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:11, 4.16it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.21it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.29it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.35it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.38it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.41it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.36it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.32it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.34it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.37it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.36it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:15<00:07, 4.39it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.37it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.41it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.42it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.42it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:16<00:06, 4.40it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.42it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.43it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:14, 1.85it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:11, 2.24it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:09, 2.64it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:08, 2.99it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.32it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:06, 3.54it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.72it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.88it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 3.96it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.09it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.20it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.27it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.30it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.35it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.39it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.39it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.40it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.43it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.46it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.45it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.46it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.46it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.42it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:23<00:00, 4.43it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.45it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.47it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.45it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.45it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.03it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.40it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.43it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.44it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.44it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.40it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.41it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.40it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:03<00:51, 1.76it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:03<00:41, 2.15it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:03<00:34, 2.55it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:03<00:30, 2.93it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:04<00:26, 3.26it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:04<00:24, 3.56it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:04<00:22, 3.79it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:04<00:21, 3.97it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:04<00:20, 4.09it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.16it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:05<00:19, 4.23it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.29it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:05<00:18, 4.36it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.35it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.37it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:17, 4.39it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.42it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.43it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.45it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.44it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:16, 4.41it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.42it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.44it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.46it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.48it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.50it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.48it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.46it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.47it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.48it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.48it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.44it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.42it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.44it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.43it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.43it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.45it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.39it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.39it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.41it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:13<00:27, 1.88it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:13<00:21, 2.28it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:13<00:18, 2.66it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:13<00:15, 3.02it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:14<00:14, 3.34it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:14<00:12, 3.61it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:14<00:11, 3.84it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.00it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:14<00:10, 4.12it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.25it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.30it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.35it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.39it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.43it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.45it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.45it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.44it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.38it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.37it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.38it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.41it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.42it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.36it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.36it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.38it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.41it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.43it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.44it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.43it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.44it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.43it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.42it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.42it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.43it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:03, 4.41it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.41it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.42it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.41it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:06, 1.87it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:23<00:05, 2.26it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:23<00:04, 2.65it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:23<00:03, 3.02it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.33it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:02, 3.59it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:24<00:01, 3.78it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:24<00:01, 3.97it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:24<00:01, 4.10it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.20it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.28it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.34it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.38it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.42it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.89it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.47it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.47it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.43it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:21, 4.45it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.43it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.44it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.46it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:20, 4.47it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.45it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.46it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.47it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.47it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.46it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.46it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.46it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.46it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.45it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.43it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.43it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.44it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.27it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.29it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.33it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:06<00:40, 1.85it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:06<00:33, 2.22it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:06<00:28, 2.56it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:07<00:25, 2.90it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:07<00:22, 3.22it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:07<00:20, 3.50it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:07<00:18, 3.73it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:08<00:17, 3.91it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.04it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:08<00:16, 4.15it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:08<00:15, 4.21it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:09<00:15, 4.30it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.35it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.40it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:09<00:14, 4.42it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:13, 4.43it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.42it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.42it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:13, 4.44it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:12, 4.46it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.46it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.47it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.47it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.48it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:11, 4.46it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.45it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.45it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.46it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:10, 4.42it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.43it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.45it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.46it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.46it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.46it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.48it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.50it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:08, 4.46it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:14<00:08, 4.47it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.47it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:16<00:19, 1.88it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:16<00:15, 2.27it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:16<00:13, 2.66it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:11, 3.02it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:17<00:09, 3.34it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.62it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:17<00:08, 3.81it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:07, 3.99it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:18<00:07, 4.14it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.22it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.28it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.32it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.36it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.39it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:05, 4.42it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.45it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:19<00:04, 4.45it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.44it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.46it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:20<00:04, 4.46it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:20<00:03, 4.49it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.49it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.49it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.49it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.44it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:21<00:02, 4.40it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.37it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.38it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.40it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:22<00:01, 4.42it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.43it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.43it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.39it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:23<00:00, 4.42it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:23<00:00, 4.42it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.42it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.42it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.40it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.06it/s]
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
1%| | 1/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.38it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.28it/s]
3%|▎ | 3/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.32it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:22, 4.32it/s]
5%|▌ | 5/100 [00:01<00:22, 4.30it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.34it/s]
7%|▋ | 7/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.34it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:01<00:21, 4.35it/s]
9%|▉ | 9/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.38it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.37it/s]
11%|█ | 11/100 [00:02<00:20, 4.38it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.41it/s]
13%|█▎ | 13/100 [00:02<00:19, 4.43it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.44it/s]
15%|█▌ | 15/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.44it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:03<00:19, 4.40it/s]
17%|█▋ | 17/100 [00:03<00:18, 4.41it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.43it/s]
19%|█▉ | 19/100 [00:04<00:18, 4.45it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.46it/s]
21%|██ | 21/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.47it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:04<00:17, 4.46it/s]
23%|██▎ | 23/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.45it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:05<00:17, 4.47it/s]
25%|██▌ | 25/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.49it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:05<00:16, 4.47it/s]
27%|██▋ | 27/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.46it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:06<00:16, 4.48it/s]
29%|██▉ | 29/100 [00:06<00:15, 4.47it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:06<00:15, 4.45it/s]
31%|███ | 31/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.46it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:07<00:15, 4.47it/s]
33%|███▎ | 33/100 [00:07<00:14, 4.49it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:07<00:14, 4.49it/s]
35%|███▌ | 35/100 [00:07<00:14, 4.49it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.44it/s]
37%|███▋ | 37/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.43it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:08<00:14, 4.42it/s]
39%|███▉ | 39/100 [00:09<00:32, 1.87it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:10<00:26, 2.27it/s]
41%|████ | 41/100 [00:10<00:22, 2.65it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:10<00:19, 3.02it/s]
43%|████▎ | 43/100 [00:10<00:17, 3.28it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:11<00:16, 3.48it/s]
45%|████▌ | 45/100 [00:11<00:14, 3.70it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:11<00:13, 3.90it/s]
47%|████▋ | 47/100 [00:11<00:13, 4.05it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:11<00:12, 4.11it/s]
49%|████▉ | 49/100 [00:12<00:12, 4.18it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.19it/s]
51%|█████ | 51/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.26it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:12<00:11, 4.32it/s]
53%|█████▎ | 53/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.35it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.39it/s]
55%|█████▌ | 55/100 [00:13<00:10, 4.42it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.43it/s]
57%|█████▋ | 57/100 [00:13<00:09, 4.38it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.30it/s]
59%|█████▉ | 59/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.28it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.26it/s]
61%|██████ | 61/100 [00:14<00:09, 4.21it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:15<00:09, 4.19it/s]
63%|██████▎ | 63/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.17it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.13it/s]
65%|██████▌ | 65/100 [00:15<00:08, 4.15it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:16<00:08, 4.18it/s]
67%|██████▋ | 67/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.18it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.16it/s]
69%|██████▉ | 69/100 [00:16<00:07, 4.13it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.12it/s]
71%|███████ | 71/100 [00:17<00:07, 4.13it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.15it/s]
73%|███████▎ | 73/100 [00:17<00:06, 4.12it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.11it/s]
75%|███████▌ | 75/100 [00:18<00:06, 4.06it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:18<00:05, 4.10it/s]
77%|███████▋ | 77/100 [00:19<00:12, 1.79it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:20<00:10, 2.16it/s]
79%|███████▉ | 79/100 [00:20<00:08, 2.54it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:20<00:06, 2.91it/s]
81%|████████ | 81/100 [00:20<00:05, 3.25it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:21<00:05, 3.51it/s]
83%|████████▎ | 83/100 [00:21<00:04, 3.74it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:21<00:04, 3.90it/s]
85%|████████▌ | 85/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.04it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:21<00:03, 4.17it/s]
87%|████████▋ | 87/100 [00:22<00:03, 4.26it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.32it/s]
89%|████████▉ | 89/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.37it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:22<00:02, 4.39it/s]
91%|█████████ | 91/100 [00:23<00:02, 4.36it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.40it/s]
93%|█████████▎| 93/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.42it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.43it/s]
95%|█████████▌| 95/100 [00:23<00:01, 4.45it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.46it/s]
97%|█████████▋| 97/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.47it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.45it/s]
99%|█████████▉| 99/100 [00:24<00:00, 4.46it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 4.46it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:25<00:00, 3.99it/s]
print(
f'Largest revenue: {largest_revenue:.1f} obtained with '
f'factor {factors[max_index]:.1f}'
)
Largest revenue: 3062.4 obtained with factor 1.2
if can_plot:
# We plot the results
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(factors, rev, label="Revenues")
ax.plot(factors, lower, label="Lower bound of the CI")
ax.plot(factors, upper, label="Upper bound of the CI")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
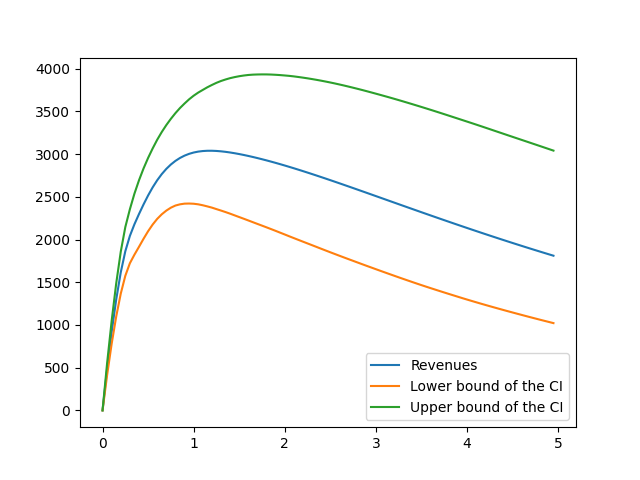
Total running time of the script: (22 minutes 32.842 seconds)