Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Calculation of willingness to pay¶
We calculate and plot willingness to pay. Details about this example are available in Section 4 of Bierlaire (2018) Calculating indicators with PandasBiogeme
Michel Bierlaire, EPFL Sat Jun 28 2025, 21:00:12
import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from IPython.core.display_functions import display
from biogeme.biogeme import BIOGEME
from biogeme.results_processing import EstimationResults
try:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
can_plot = True
except ModuleNotFoundError:
can_plot = False
from biogeme.expressions import Derive
from biogeme.data.optima import read_data, normalized_weight
from scenarios import scenario
Obtain the specification for the default scenario The definition of the scenarios is available in Specification of a nested logit model.
v, _, _, _ = scenario()
v_pt = v[0]
v_car = v[1]
Calculation of the willingness to pay using derivatives.
wtp_pt_time = Derive(v_pt, 'TimePT') / Derive(v_pt, 'MarginalCostPT')
wtp_car_time = Derive(v_car, 'TimeCar') / Derive(v_car, 'CostCarCHF')
Formulas to simulate.
simulate = {
'weight': normalized_weight,
'WTP PT time': wtp_pt_time,
'WTP CAR time': wtp_car_time,
}
Read the data
database = read_data()
Create the Biogeme object.
the_biogeme = BIOGEME(database, simulate)
Read the estimation results from the file.
try:
results = EstimationResults.from_yaml_file(
filename='saved_results/b02estimation.yaml'
)
except FileNotFoundError:
sys.exit(
'Run first the script b02estimation.py in order to generate '
'the file b02estimation.yaml.'
)
simulated_values is a Pandas dataframe with the same number of rows as the database, and as many columns as formulas to simulate.
simulated_values = the_biogeme.simulate(results.get_beta_values())
display(simulated_values)
weight WTP PT time WTP CAR time
0 0.893779 0.038431 0.038431
1 0.868674 0.038431 0.038431
2 0.868674 0.038431 0.038431
3 0.965766 0.111009 0.111009
4 0.868674 0.038431 0.038431
... ... ... ...
1894 2.053830 0.038431 0.038431
1895 0.868674 0.111009 0.111009
1896 0.868674 0.111009 0.111009
1897 0.965766 0.038431 0.038431
1898 0.965766 0.038431 0.038431
[1899 rows x 3 columns]
Note the multiplication by 60 to have the valus of time per hour and not per minute.
wtpcar = (60 * simulated_values['WTP CAR time'] * simulated_values['weight']).mean()
Calculate confidence intervals
b = results.get_betas_for_sensitivity_analysis()
Returns data frame containing, for each simulated value, the left and right bounds of the confidence interval calculated by simulation.
left, right = the_biogeme.confidence_intervals(b, 0.9)
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
2%|▏ | 2/100 [00:00<00:07, 13.91it/s]
4%|▍ | 4/100 [00:00<00:06, 14.00it/s]
6%|▌ | 6/100 [00:00<00:06, 13.85it/s]
8%|▊ | 8/100 [00:00<00:06, 13.99it/s]
10%|█ | 10/100 [00:00<00:06, 13.96it/s]
12%|█▏ | 12/100 [00:00<00:06, 13.81it/s]
14%|█▍ | 14/100 [00:01<00:06, 13.96it/s]
16%|█▌ | 16/100 [00:01<00:05, 14.01it/s]
18%|█▊ | 18/100 [00:01<00:05, 13.86it/s]
20%|██ | 20/100 [00:01<00:05, 13.97it/s]
22%|██▏ | 22/100 [00:01<00:05, 14.02it/s]
24%|██▍ | 24/100 [00:01<00:05, 13.83it/s]
26%|██▌ | 26/100 [00:01<00:05, 13.51it/s]
28%|██▊ | 28/100 [00:02<00:05, 13.11it/s]
30%|███ | 30/100 [00:02<00:05, 12.82it/s]
32%|███▏ | 32/100 [00:02<00:05, 13.00it/s]
34%|███▍ | 34/100 [00:02<00:05, 12.97it/s]
36%|███▌ | 36/100 [00:02<00:04, 13.03it/s]
38%|███▊ | 38/100 [00:02<00:04, 13.36it/s]
40%|████ | 40/100 [00:02<00:04, 13.59it/s]
42%|████▏ | 42/100 [00:03<00:04, 13.58it/s]
44%|████▍ | 44/100 [00:03<00:04, 13.73it/s]
46%|████▌ | 46/100 [00:03<00:03, 13.82it/s]
48%|████▊ | 48/100 [00:03<00:03, 13.71it/s]
50%|█████ | 50/100 [00:03<00:03, 13.88it/s]
52%|█████▏ | 52/100 [00:03<00:03, 13.70it/s]
54%|█████▍ | 54/100 [00:03<00:03, 13.52it/s]
56%|█████▌ | 56/100 [00:04<00:03, 13.70it/s]
58%|█████▊ | 58/100 [00:04<00:03, 13.90it/s]
60%|██████ | 60/100 [00:04<00:02, 13.76it/s]
62%|██████▏ | 62/100 [00:04<00:02, 13.87it/s]
64%|██████▍ | 64/100 [00:04<00:02, 13.94it/s]
66%|██████▌ | 66/100 [00:04<00:02, 13.81it/s]
68%|██████▊ | 68/100 [00:04<00:02, 13.88it/s]
70%|███████ | 70/100 [00:05<00:02, 14.02it/s]
72%|███████▏ | 72/100 [00:05<00:02, 13.69it/s]
74%|███████▍ | 74/100 [00:05<00:01, 13.79it/s]
76%|███████▌ | 76/100 [00:05<00:01, 13.91it/s]
78%|███████▊ | 78/100 [00:05<00:01, 13.84it/s]
80%|████████ | 80/100 [00:05<00:01, 13.82it/s]
82%|████████▏ | 82/100 [00:05<00:01, 13.87it/s]
84%|████████▍ | 84/100 [00:06<00:01, 13.70it/s]
86%|████████▌ | 86/100 [00:06<00:01, 13.88it/s]
88%|████████▊ | 88/100 [00:06<00:00, 13.92it/s]
90%|█████████ | 90/100 [00:06<00:00, 13.72it/s]
92%|█████████▏| 92/100 [00:06<00:00, 13.87it/s]
94%|█████████▍| 94/100 [00:06<00:00, 14.00it/s]
96%|█████████▌| 96/100 [00:06<00:00, 13.90it/s]
98%|█████████▊| 98/100 [00:07<00:00, 13.93it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:07<00:00, 13.89it/s]
100%|██████████| 100/100 [00:07<00:00, 13.73it/s]
Lower bounds of the confidence intervals
display(left)
weight WTP PT time WTP CAR time
0 0.893779 0.006695 0.006695
1 0.868674 0.006695 0.006695
2 0.868674 0.006695 0.006695
3 0.965766 0.071157 0.071157
4 0.868674 0.006695 0.006695
... ... ... ...
1894 2.053830 0.006695 0.006695
1895 0.868674 0.071157 0.071157
1896 0.868674 0.071157 0.071157
1897 0.965766 0.006695 0.006695
1898 0.965766 0.006695 0.006695
[1899 rows x 3 columns]
Upper bounds of the confidence intervals
display(right)
weight WTP PT time WTP CAR time
0 0.893779 0.080166 0.080166
1 0.868674 0.080166 0.080166
2 0.868674 0.080166 0.080166
3 0.965766 0.178108 0.178108
4 0.868674 0.080166 0.080166
... ... ... ...
1894 2.053830 0.080166 0.080166
1895 0.868674 0.178108 0.178108
1896 0.868674 0.178108 0.178108
1897 0.965766 0.080166 0.080166
1898 0.965766 0.080166 0.080166
[1899 rows x 3 columns]
Lower and upper bounds of the willingness to pay.
wtpcar_left = (60 * left['WTP CAR time'] * left['weight']).mean()
wtpcar_right = (60 * right['WTP CAR time'] * right['weight']).mean()
print(
f'Average WTP for car: {wtpcar:.3g} ' f'CI:[{wtpcar_left:.3g}, {wtpcar_right:.3g}]'
)
Average WTP for car: 3.89 CI:[1.81, 6.95]
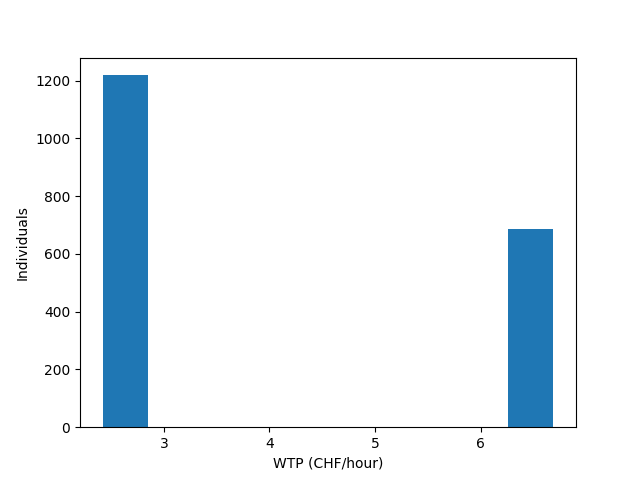
In this specific case, there are only two distinct values in the population: for workers and non workers
print(
'Unique values: ',
[f'{i:.3g}' for i in 60 * simulated_values['WTP CAR time'].unique()],
)
Unique values: ['2.31', '6.66']
Function calculating the willingness to pay for a group.
def wtp_for_subgroup(the_filter: 'pd.Series[np.bool_]') -> tuple[float, float, float]:
"""
Check the value for groups of the population. Define a function that
works for any filter to avoid repeating code.
:param the_filter: pandas filter
:return: willingness-to-pay for car and confidence interval
"""
size = the_filter.sum()
sim = simulated_values[the_filter]
total_weight = sim['weight'].sum()
weight = sim['weight'] * size / total_weight
_wtpcar = (60 * sim['WTP CAR time'] * weight).mean()
_wtpcar_left = (60 * left[the_filter]['WTP CAR time'] * weight).mean()
_wtpcar_right = (60 * right[the_filter]['WTP CAR time'] * weight).mean()
return _wtpcar, _wtpcar_left, _wtpcar_right
Full time workers.
a_filter = database.dataframe['OccupStat'] == 1
w, l, r = wtp_for_subgroup(a_filter)
print(f'WTP car for workers: {w:.3g} CI:[{l:.3g}, {r:.3g}]')
WTP car for workers: 6.66 CI:[4.27, 10.7]
Females.
a_filter = database.dataframe['Gender'] == 2
w, l, r = wtp_for_subgroup(a_filter)
print(f'WTP car for females: {w:.3g} CI:[{l:.3g}, {r:.3g}]')
WTP car for females: 3.09 CI:[1.1, 5.87]
Males.
a_filter = database.dataframe['Gender'] == 1
w, l, r = wtp_for_subgroup(a_filter)
print(f'WTP car for males : {w:.3g} CI:[{l:.3g}, {r:.3g}]')
WTP car for males : 4.89 CI:[2.7, 8.3]
We plot the distribution of WTP in the population. In this case, there are only two values
if can_plot:
plt.hist(
60 * simulated_values['WTP CAR time'],
weights=simulated_values['weight'],
)
plt.xlabel('WTP (CHF/hour)')
plt.ylabel('Individuals')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 8.085 seconds)